 |
|||

|
|||
| Home Research Publications People Conference Presentations Instrument Shop Links Internal | |||
Jet Energy Scale
Jet Physics
|
|
The CMS detector is built around a huge solenoid magnet.
This takes the form of a cylindrical coil
of superconducting cable that generates a magnetic field of 4 teslas, about 100 000 times that of the Earth.
The magnetic field is confined by a steel 'yoke' that forms the bulk of the detector's weight of 12 500 tonnes.
An unusual feature of the CMS detector is that instead of being built in-situ underground, like the other giant
detectors of the LHC experiments, it was constructed on the surface, before being lowered underground in 15
sections and reassembled.
More than 2000 scientists collaborate in CMS.
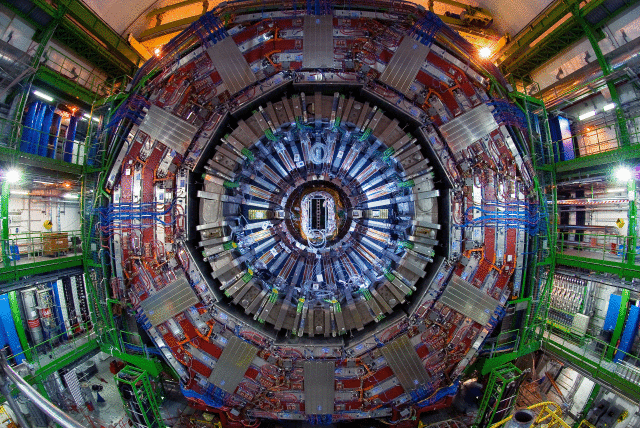 CMS detector. Jet Energy ScaleJets+METJets+MET Topology GroupPhysics Validation Group for Jets+METStatisticsCMS Statistics CommitteeSUSY PhysicsCMS SUSY Physics GroupForward PhysicsCMS Forward Physics GroupCDFCollider Detector at FermilabCDF, the Collider Detector at Fermilab, is an experiment at Fermi National Laboratory near Chicago, which is currently home to the world's most powerful particle accelerator called the Tevatron. The Tevatron accelerates protons and antiprotons close to the speed of light, and then makes them collide head-on inside the CDF detector. The CDF detector is used to study the products of such collisions; by doing this we try to reconstruct what happened in the collision and ultimately try to figure out how matter is put together and what forces nature uses to create the world around us!
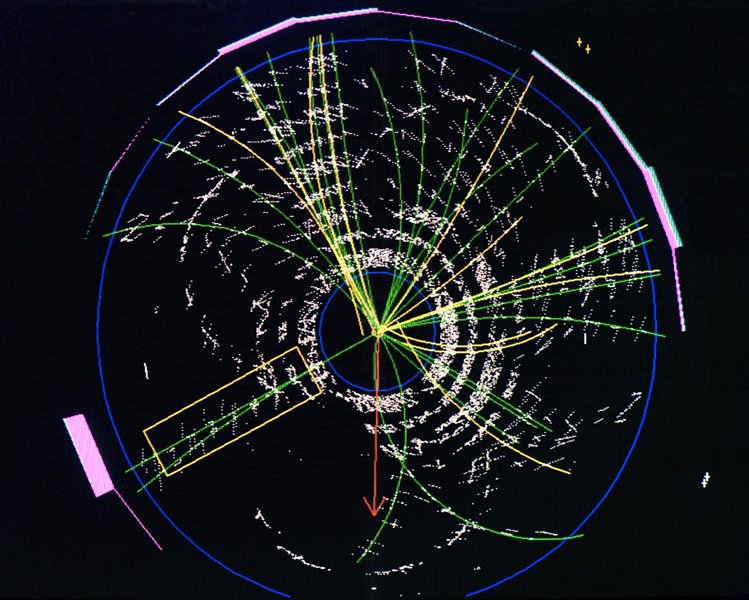 CDF Top Event in 1995 on Computer Screen. DiffractionForward Detectors at CDFSelected Diffractive Physics PublicationsTop PhysicsCDF Top Physics GroupDiscovery of the Top Quark at CDFJet PhysicsCDF QCD Physics GroupCDF Jet Energy Resolution GroupHiggs PhysicsCDF Higgs Physics Group
Statistics CommitteeCDF Statistics CommitteeHardware ProjectsSelected papers MiniPlug calorimeter during assembly. PhenomenologySelected papers |
|